How to Convert DWG to KML and DXF to KML
Most people who use the Propeller Platform to measure and manage their worksites also work with different drone surveying software and supporting programs. To help you better understand our Platform’s many tools, we’ve put together write-ups on our most popular data queries.
Today, we’re covering how to convert DWG to KML and how to convert DXF to KML using QGIS. This how-to is intended for users who:
- Have QGIS installed on their computers
- Are working with a DWG/DXF file with elevation
- Have a site using global projections (local grid isn’t supported by QGIS yet)
Did you know that you can import DXFs directly into the Propeller Platform? Learn more here.
Choose your global projections
Once you’ve dragged and dropped your DXG/DXF file into QGIS, you need to choose your site’s correct projection information. There will be an extensive list to choose from. If you’re not sure what the projections are for this site, reach out to the person in charge of the DWG/DXF file.
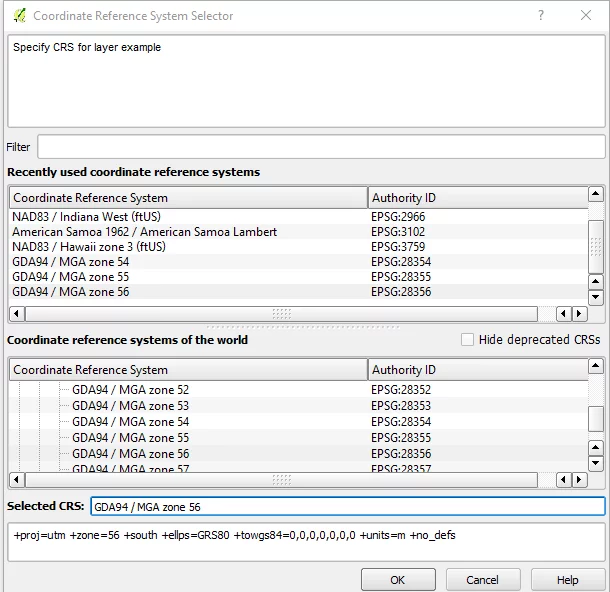
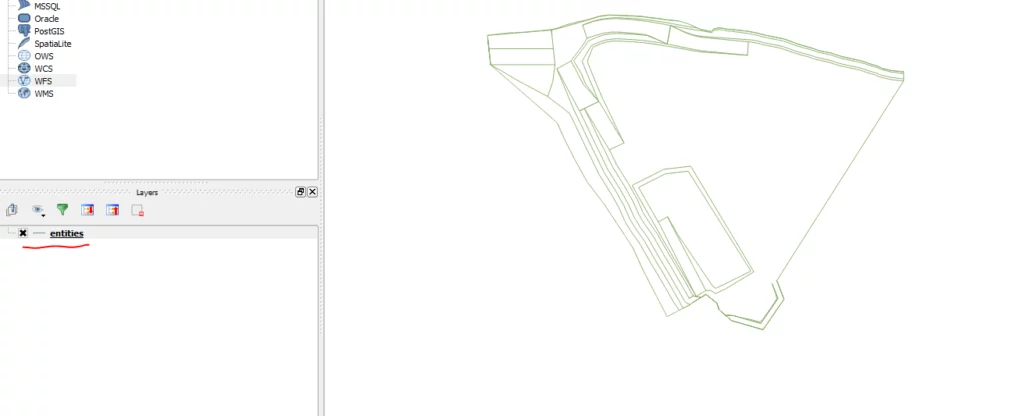
Once you’ve chosen from that list, you’ll see something like this:
Saving your converted file
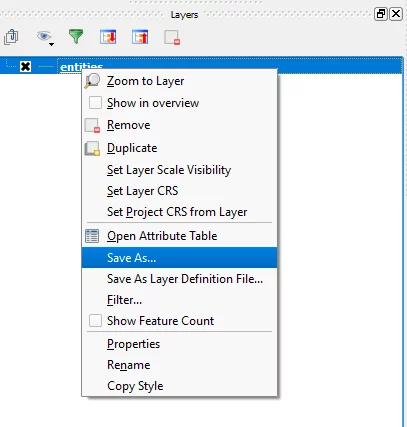
When you reach the screen above, navigate to the “Entities” heading on the bottom left area. Then right-click on “entities” and select “Save As…” from the menu that appears (shown below).
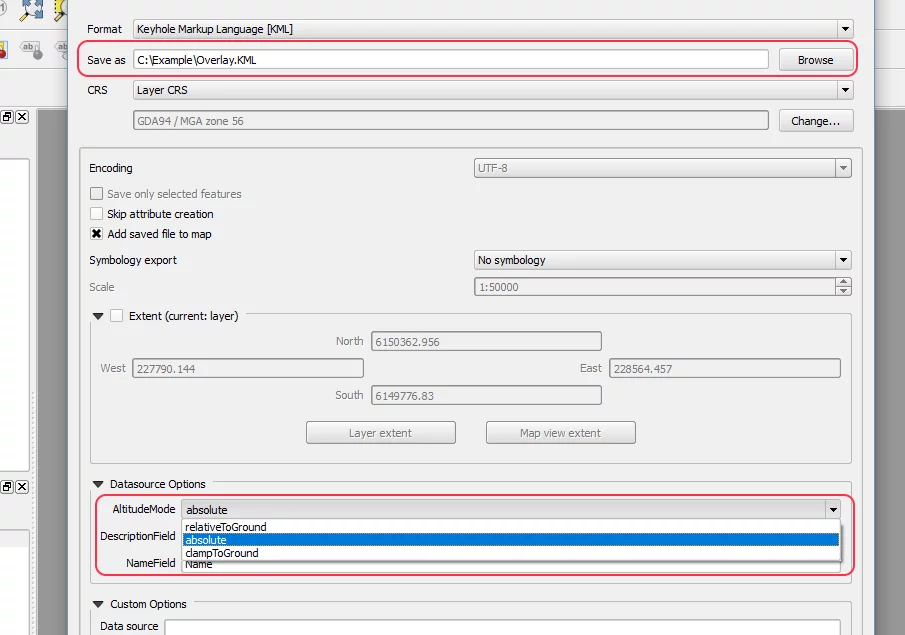
Select the location where you want to save the KML file. You can either manually type the location or browse your computer.
Further down that “Save As…” popup, you’ll find a section called Datasource Options. There, set your Altitude Mode to “absolute.” Then save your file.
Using a KML in Propeller
Once saved, you’ve successfully converted your DWG/DXF into a KML file. Once your file is in KML format, you can upload your data to your intended program.
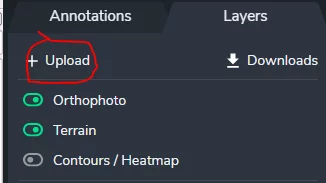
If you’re using the Propeller Platform, you can upload a DXF directly (or the KML) as a Layer and visualize over a 3D survey of your site.
To do this, simply navigate to Layers > Upload in the Propeller Platform portal. Your overlays will appear on your 3D survey.

This lets you visualize your DXF or KML data in 3D so you can see how it relates to your site, rather than relying on numbers and values alone.